Cultural Property of Japan
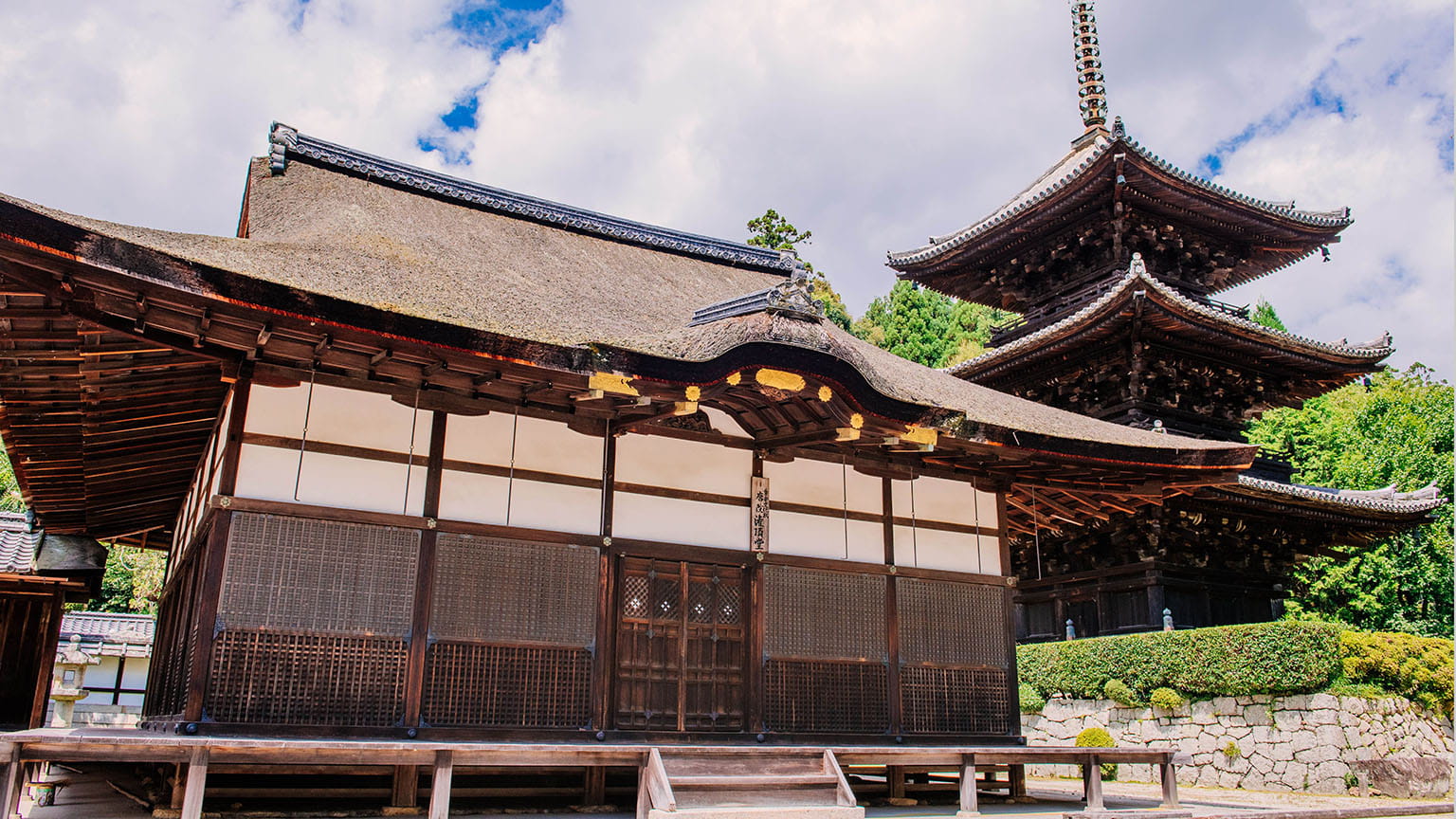
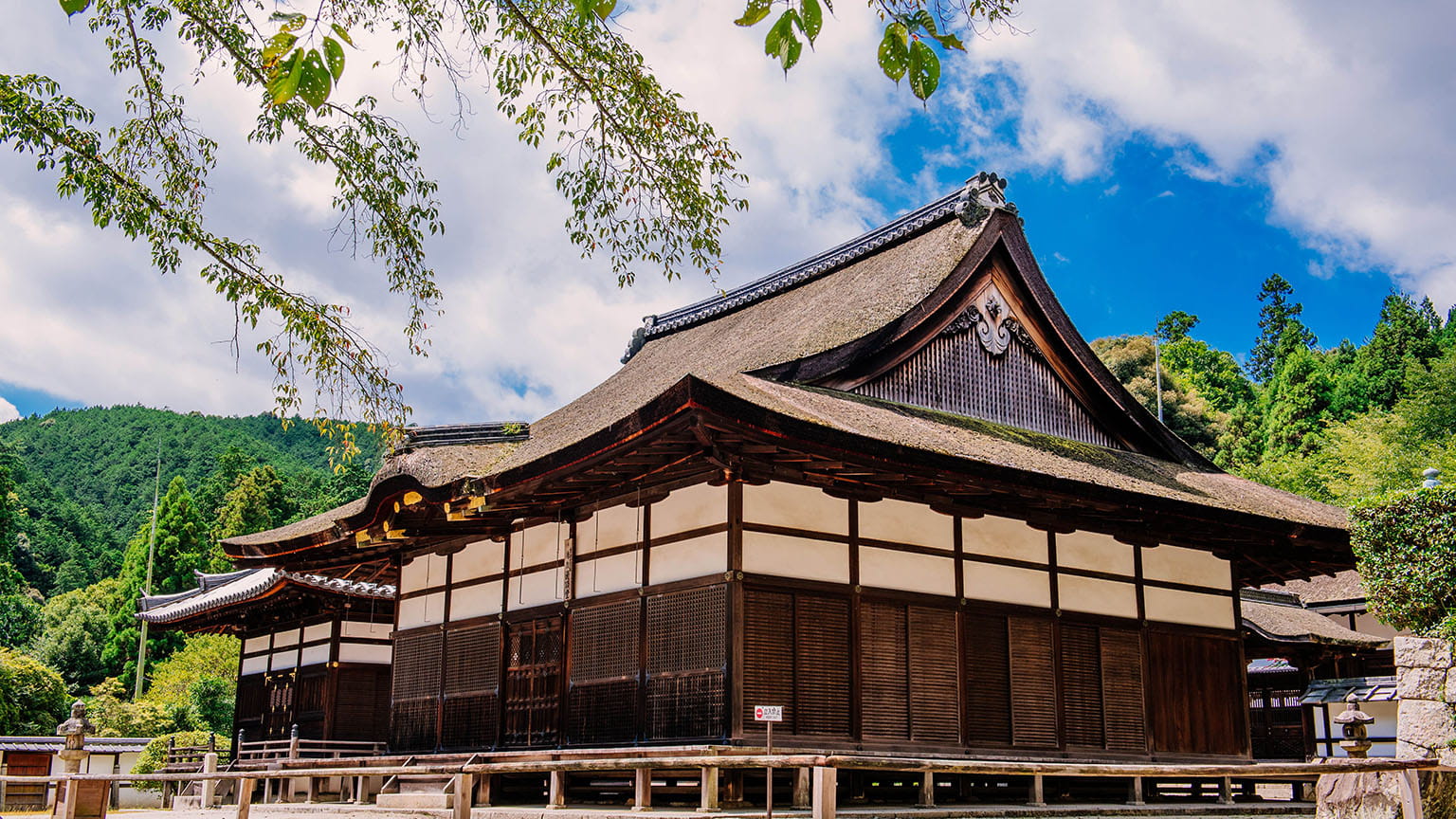
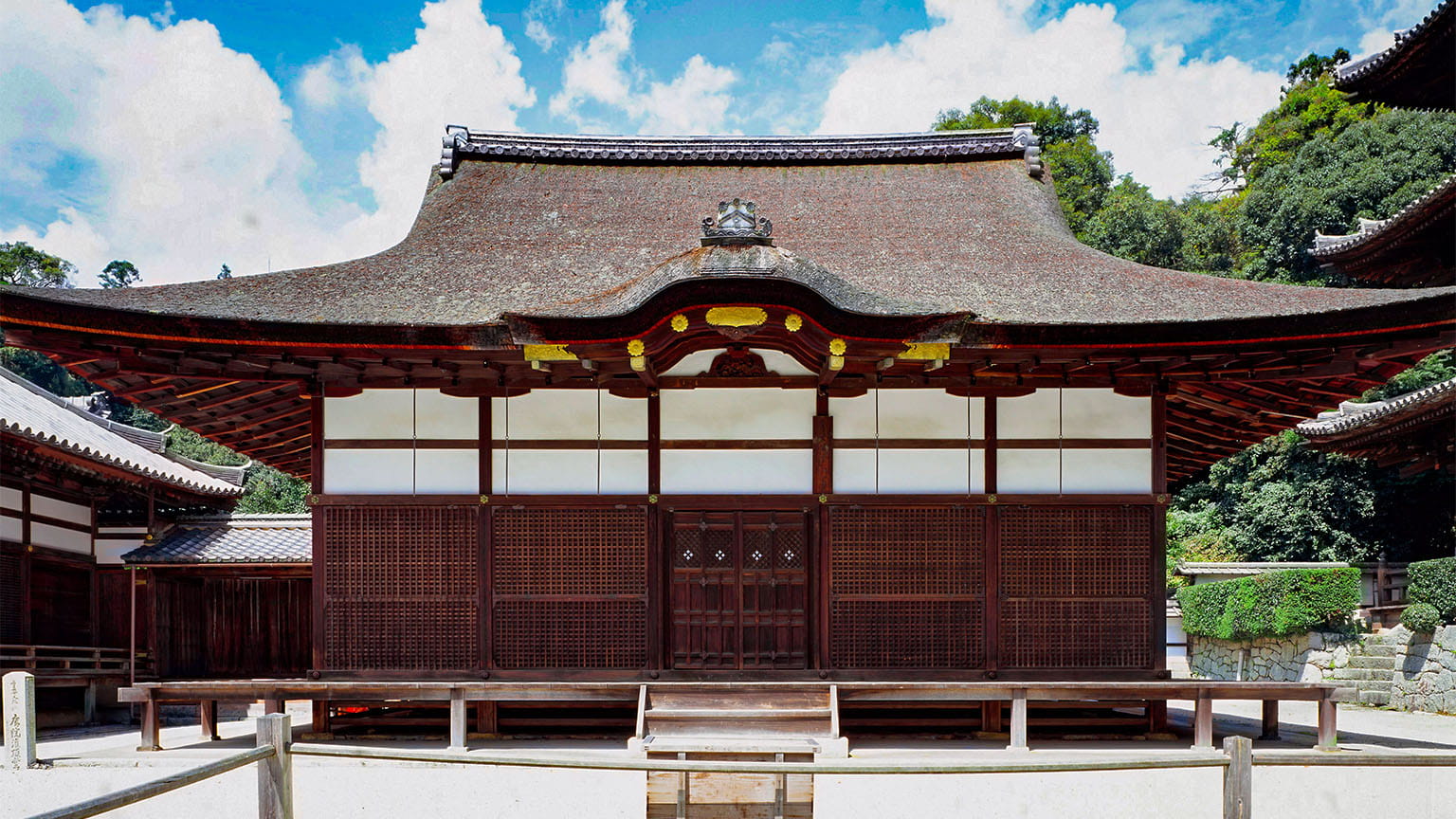
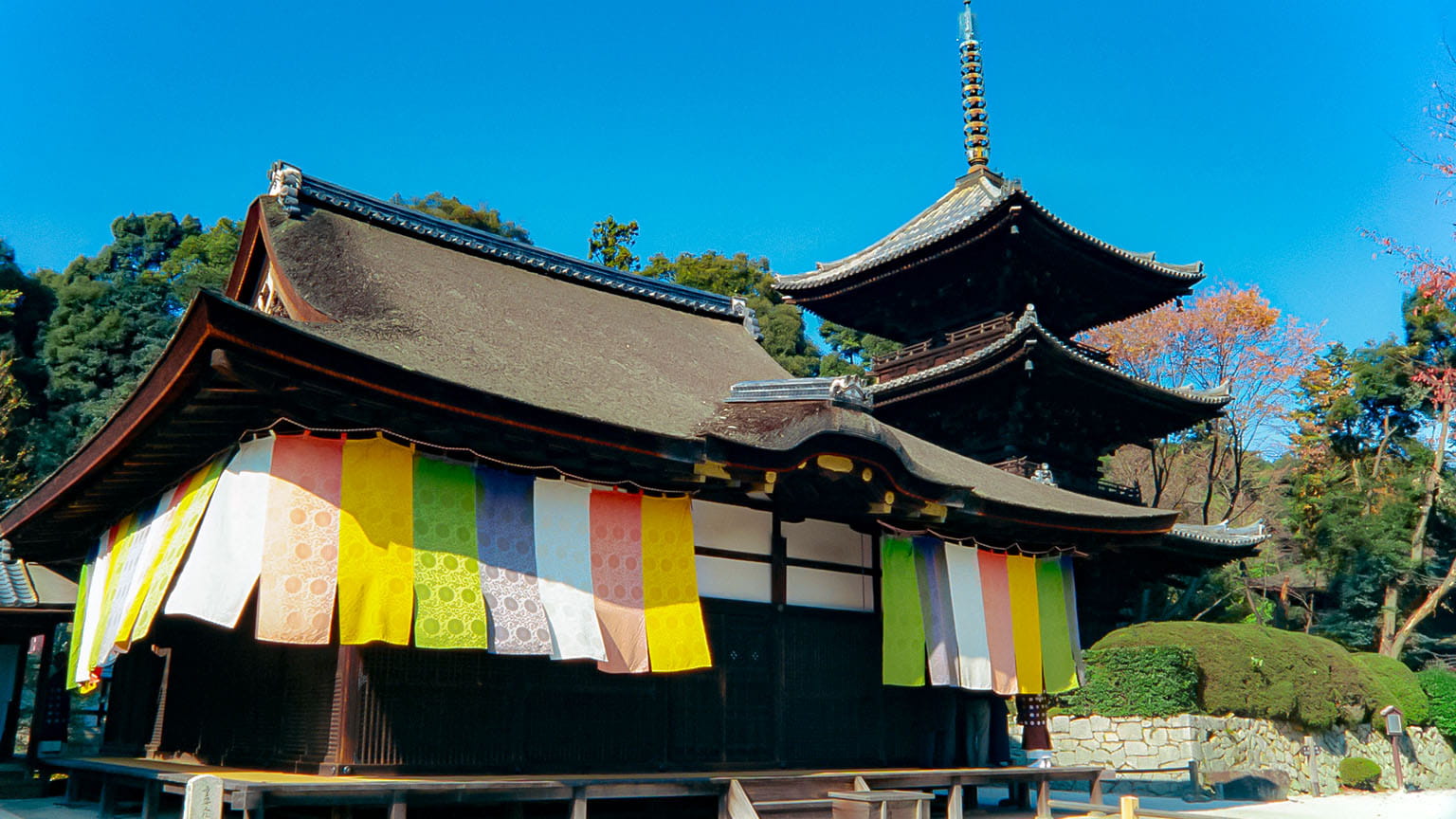
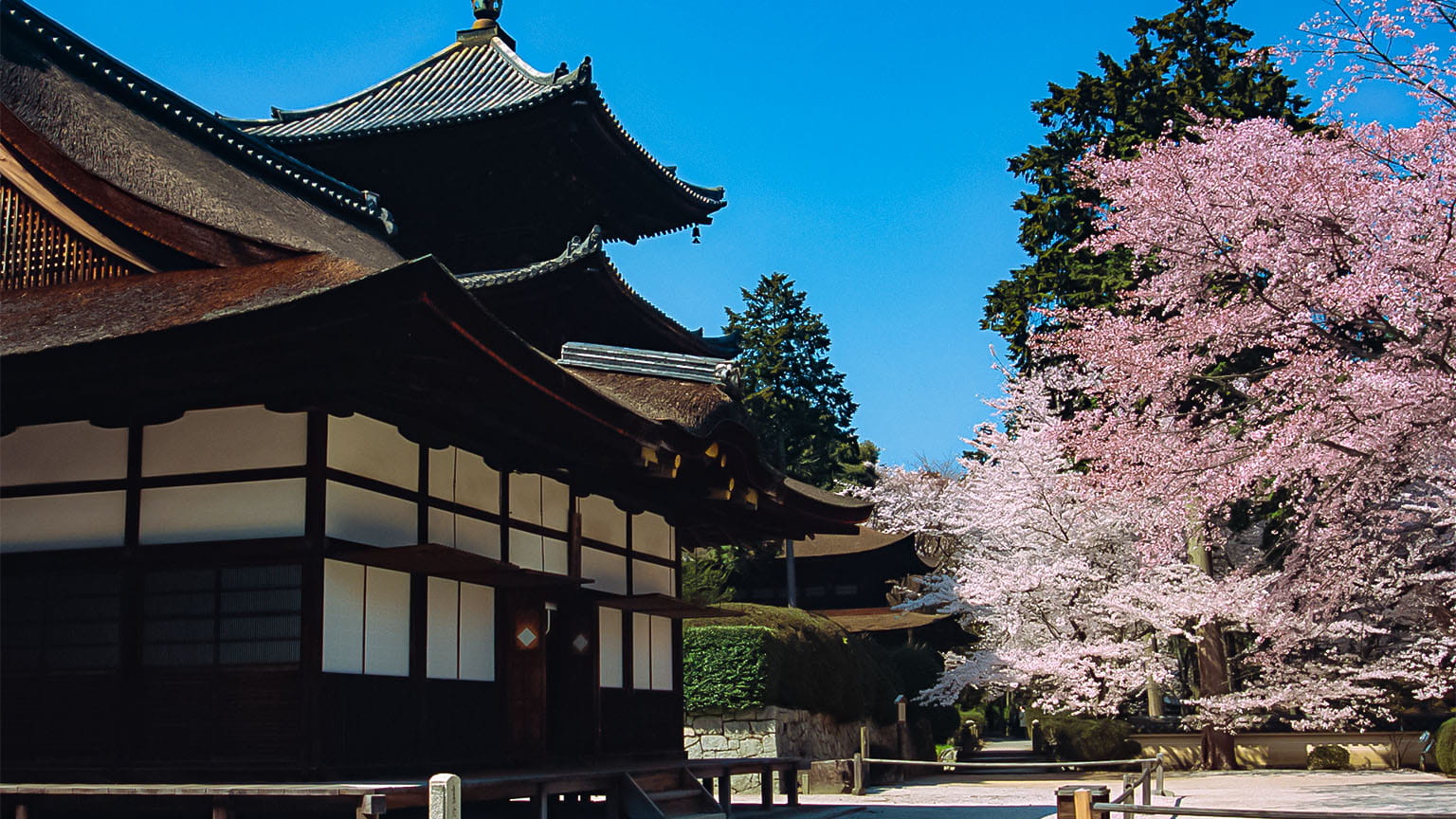
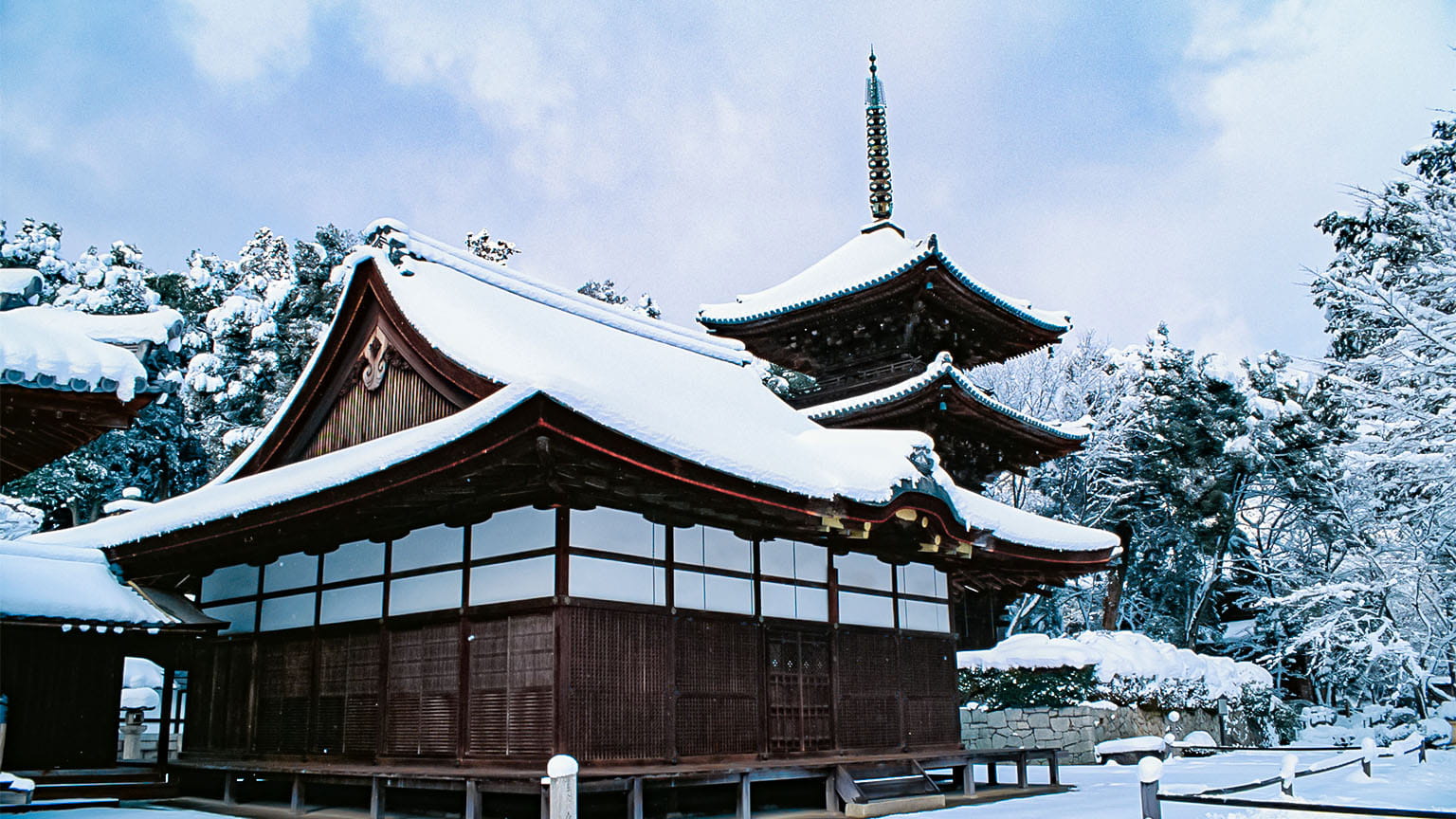
Toin Kanjodo Hall
READER
The Toin is a subsection of and the holiest part of Miidera Temple, containing the mausoleum of Chisho Daishi, the temple’s founder.
The name of the Toin is derived from the ritual implements and tomes of scriptures brought back by Chisho Daishi from Tang China, pronounced “To” in Japanese. The Emperor Seiwa, on learning that Chisho Daishi needed a place to store these artifacts, granted him the Jijuden central pavilion from the Imperial Palace. In addition to serving as a storehouse, and mausoleum, the Toin is also a center for training in denpokanjo, a ritual used to officially ordain master monks.
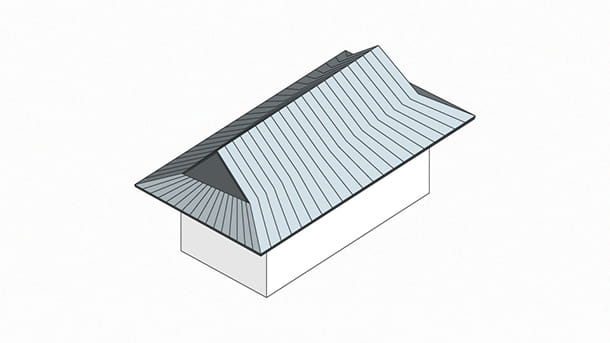
The current Kanjodo Hall was rebuilt in the Keicho era (1596-1615) as a place of worship for the Daishido Hall and as a center for training in denpokanjo, which teaches the secrets of esoteric Buddhism. It has irimoya-zukuri hip-and-gable roofs, cypress bark roofing, and cusped karahafu gable eaves on the central part of the façade. As a whole, the building showcases an elegant residential style that first appeared in the Heian period (794-1185) and developed over time.
- −
- Momoyama Period
Please rate this cultural heritage introduction page.
-
-
Satisfaction
-
-
Understanding
-
-
Recommendation
-
-
Attractiveness
-